

- FREE NETWORK VULNERABILITY SCANNER FULL VERSION
- FREE NETWORK VULNERABILITY SCANNER FULL
- FREE NETWORK VULNERABILITY SCANNER SOFTWARE
Why Should We Use Vulnerability Assessment Scanning Software?.
FREE NETWORK VULNERABILITY SCANNER SOFTWARE
FREE NETWORK VULNERABILITY SCANNER FULL
Since the OpenVAS scanner performs a considerable number of tests, the full scan can take from 30 minutes to several hours. This will skip host discovery and just start the port scan. Note: If the scanner does not find any open ports even though you know there are, we recommend you re-running the scan with the option "Check if the host is alive" disabled. does not respond to ICMP requests) it shows zero open ports found. However, keep in mind that the scanner first attempts to detect if the host is alive or not before doing the port scan. We've configured OpenVAS to scan for a default list of ports including the most common 6000 ports ( TCP and UDP). For example, if a previous plugin detects the FTP service running on port 2121, it will run all the FTP-related plugins on that port. This one includes most of the NVTs and is updated to use the data collected by the previous plugins. While OpenVAS has multiple predefined policies, our scanner uses the one called Full and Fast.
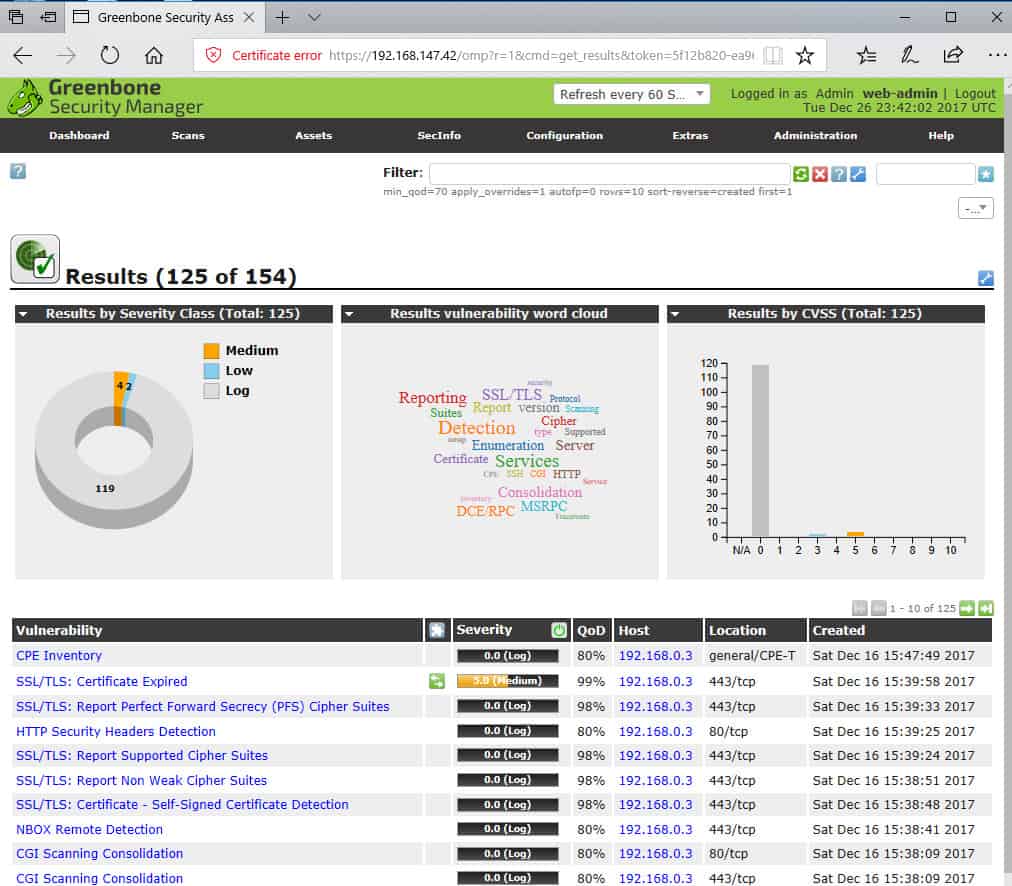
Req = https_get(request:req1, port:port) Req1 = http_get(item:"/system/console?version=1.5", port:port) Send(socket:soc, data:string(request,"\r\n")) Soc = open_sock_tcp(port, transport:ENCAPS_SSLv23) Script_dependencies("http_version.nasl") Script_name("Fortinet Fortigate console management detection") # This script is released under the GNU GPL v2 # This script was written by David Maciejak It's called fortigate_detect.nasl and shows if the target device is a Fortigate Firewall: It has more than 57000 active plugins to detect a large number of vulnerabilities for many services and applications.įor example, here is how a simple NVT looks like. OpenVAS implements each test in a plugin called NVT (Network Vulnerability Test). OpenVAS is currently developed and maintained by Greenbone Networks with support from the community. OpenVAS is a fork of the old Nessus scanner, performed in 2005 when Nessus became a commercial product. This is the complete list of Sniper detection modules currently available in our Network Scanner: They are added on top of the standard OpenVAS scan in order to provide rapid detection of the most critical vulnerabilities from high-profile software. The Sniper modules are custom vulnerability checks developed by our team. The engine is running in a distributed environment and it can perform multiple parallel scans. We have pre-configured and fine-tuned OpenVAS on our servers and have also added a very simple interface on top of its complex functionalities. Depending on the response, the scanner reports the service as vulnerable or not. OpenVAS does vulnerability detection by connecting to each network service and sending crafted packets to make them respond in certain ways. It actively detects thousands of vulnerabilities in network services such as SMTP, DNS, VPN, SSH, RDP, VNC, HTTP, and many more.
FREE NETWORK VULNERABILITY SCANNER FULL VERSION
The Full version of the Network Vulnerability Scanner uses a mix of custom Sniper modules for high risk vulnerabilities and the well-known OpenVAS (the most advanced open source vulnerability scanner) as a scanning engine. Although this detection method is faster, it can return false positives because it relies only on the version reported by the services (which may be inaccurate). Then, based on the results returned by Nmap, our network scanner interrogates a database with known vulnerabilities to check if the specific versions of the services are affected by any issues. It starts by running Nmap to detect open ports and services. The Light version of our Network Vulnerability Scanner performs a very fast security assessment with minimum interaction with the target system. This way, the network perimeter exposes important network services such as FTP, VPN, DNS, HTTP, and more.Ī Network Vulnerability Scanner maps all the services exposed on the network perimeter and checks for potential vulnerabilities. Connecting from outside means accessing internal assets (e.g. The network perimeter of a company is the "wall" that secures internal network assets from the outside world.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
